Inhaltsübersicht
Cats use tail positions and movements to communicate mood and comfort levels—like confidence, fear, focus, irritation, or affection. The most reliable way to “read” a tail is to match the tail signal with the rest of the body (ears, eyes, posture) and the situation.
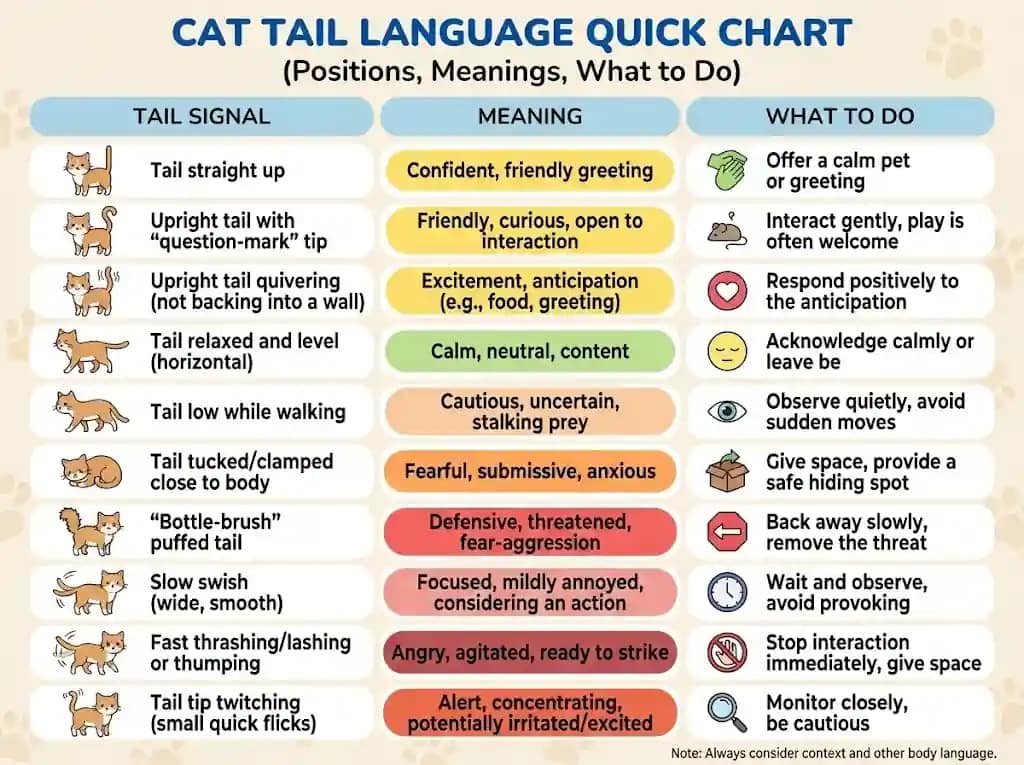
Cat Tail Language Quick Chart (Positions, Meanings, What to Do)
| Tail signal | What it usually means | What you should do |
|---|---|---|
| Tail straight up | Friendly greeting, confident mood | Greet calmly; offer gentle petting or play |
| Upright tail with “question-mark” tip | Playful, inviting, curious | Engage with a toy; let your cat approach |
| Upright tail quivering (not backing into a wall) | Excited anticipation (often at meals or greetings) | Reward with attention; check context to rule out spraying |
| Tail relaxed and level (horizontal) | Calm, neutral, at ease | Normal interaction is fine; observe baseline |
| Tail low while walking | Uncertain, cautious, stressed | Reduce pressure; give space; remove stressors |
| Tail tucked/clamped close to body | Fear, high stress, or possible pain | Do not force contact; create safety and distance |
| “Bottle-brush” puffed tail | Startled/defensive fear, high arousal | Back off; remove threat; allow Verstecken time |
| Slow swish (wide, smooth) | Focused attention (often hunting/play) | Encourage healthy play if appropriate |
| Fast thrashing/lashing or thumping | Overstimulated, irritated, warning | Stop what you’re doing; give space immediately |
| Tail tip twitching (small quick flicks) | Mild irritation OR intense focus | Check ears/eyes; pause petting or redirect to play |
A quick note from me (why this guide is practical)
Cats “talk” with their tails. Cat tail positions and movements can signal friendliness, excitement, fear, irritation—or even pain.
In this guide you’ll learn cat tail language meanings (upright tail, question-mark tip, twitching, thumping, bottle-brush, tucked tail), plus when tail behavior is a red flag worth a vet call.
Tipp: Always read the whole cat (ears, eyes, posture, and environment), not the tail alone.
Common Cat Tail Questions (Quick Meanings)
Cats “talk” with their tails in ways that are surprisingly consistent—once you know what to look for. If you just want quick answers, use the chart below, then jump into the deeper explanations later in the guide.
Quick Cat Tail Language Chart (at a glance)
Tail straight up → friendly/confident greeting
Question-mark tip → playful/inviting mood
Tail quivering/vibrating → excitement (or spraying if backing up to a surface)
Slow swish → focused “hunting/thinking” mode
Fast thumping/lashing → irritation/overstimulation (a clear warning)
Puffed “bottle brush” tail → fear/defensive arousal
Tail tucked/clamped → fear/stress (or possible pain if persistent)
Tail-tip twitching → mild irritation or intense focus (context matters)
Why do cats wag their tails? It’s not like dogs
When people ask why cats “wag” their tails, they’re usually seeing arousal, not friendly excitement like a dog. In cats, tail swishing often means the cat is focused, conflicted, oder overstimulated.
Common reasons: watching prey/toys, getting annoyed during petting, frustration, or mild agitation.
Was ist zu tun? pause petting, give space, or redirect with a toy if they’re in hunting mode.
When to worry: if tail-wagging is suddenly new and paired with hiding, aggression, or pain signs, consider a vet check.
Cat tail thumping on the floor: what it means
A cat thumping their tail against the floor is one of the clearest “I’m getting irritated” signals. Think of it as a warning that your cat is nearing their limit—especially during petting or when something is bothering them.
Common reasons: overstimulation, frustration (can’t reach something), another pet in their space.
Was ist zu tun? stop the interaction, reduce stimulation, and give your cat a break.
When to worry: if tail thumping is frequent along with unusual sensitivity, limping, or behavior changes, rule out pain.
Cat tail quivering: excitement vs spraying
A raised tail that quivers often means your cat is thrilled—common during greetings or right before food. But quivering can also appear with urine marking if your cat backs up to a wall or furniture.
Excitement clues: relaxed body, friendly approach, rubbing, no backing-to-surface.
Spraying clues: backing up, tail straight up, quiver + possible urine odor.
Was ist zu tun? check context; if marking is possible, clean with enzymatic cleaner and address stressors.
When to worry: new marking behavior can be stress- or health-related.
Cat tail vibrating while purring
A “vibrating” tail while purring is usually a sign of happy excitement—like your cat is emotionally overflowing during affection or greeting. Many cats do this when they’re pleased to see you or anticipating something good.
Was ist zu tun? keep interaction calm and positive—gentle petting, soft voice, or a short play session.
Watch for: if the cat is vibrating while backing up to objects, review the quiver vs spraying section above.
When to worry: if vibration comes with sudden sensitivity, skin rippling, or agitation, check the red flag section later.
Cat tail twitching tip meaning
If only the tip of the tail is twitching, your cat is often in a state of mild stimulation—either intense focus (watching prey/toy) or mild irritation (unsure or annoyed).
Focus clues: forward ears, locked gaze, crouching/poised to abspringen.
Irritation clues: ears turning back, side-eye, tense body, stopping interaction.
Was ist zu tun? if you’re petting, pause; if they’re hunting-focused, offer appropriate play.
When to worry: sudden twitching with pain signs or aggression may justify a vet call.
Tail down while walking: stress vs low confidence
A tail held low while walking often signals uncertainty, Vorsicht, oder Stress—especially in new environments or around unfamiliar sounds/people/pets.
Mild caution: tail low but body still moving/curious.
Fear/stress: tail tucked, crouching, freezing, hiding.
Was ist zu tun? give space, reduce stressors, let your cat approach at their own pace.
When to worry: if a normally confident cat keeps the tail low for days, consider stress or pain.
Why is my cat’s tail puffed up? Fear vs play
A puffed-up “bottle brush” tail means high arousal—most often fear or defensive aggression. Kittens sometimes puff up during play, but adult puffing usually means “back off.”
Fear clues: arched back, ears pinned, hissing/growling, hiding.
Play clues: bouncy movement, loose body, quick recovery, no hiding.
Was ist zu tun? give space and remove the trigger if possible.
When to worry: repeated puffing without obvious triggers may indicate chronic stress.
Why does my cat chase or bite its tail?
Kittens may chase tails for fun, but adult tail chasing or biting can signal something else.
Häufige Ursachen: fleas/allergies (itch), stress/anxiety, pain, or (rarely) feline hyperesthesia episodes.
Was ist zu tun? check for fleas/skin irritation, reduce stress, and track triggers.
When to worry: self-injury, sudden adult onset, skin rippling episodes, or aggression warrants a vet visit.
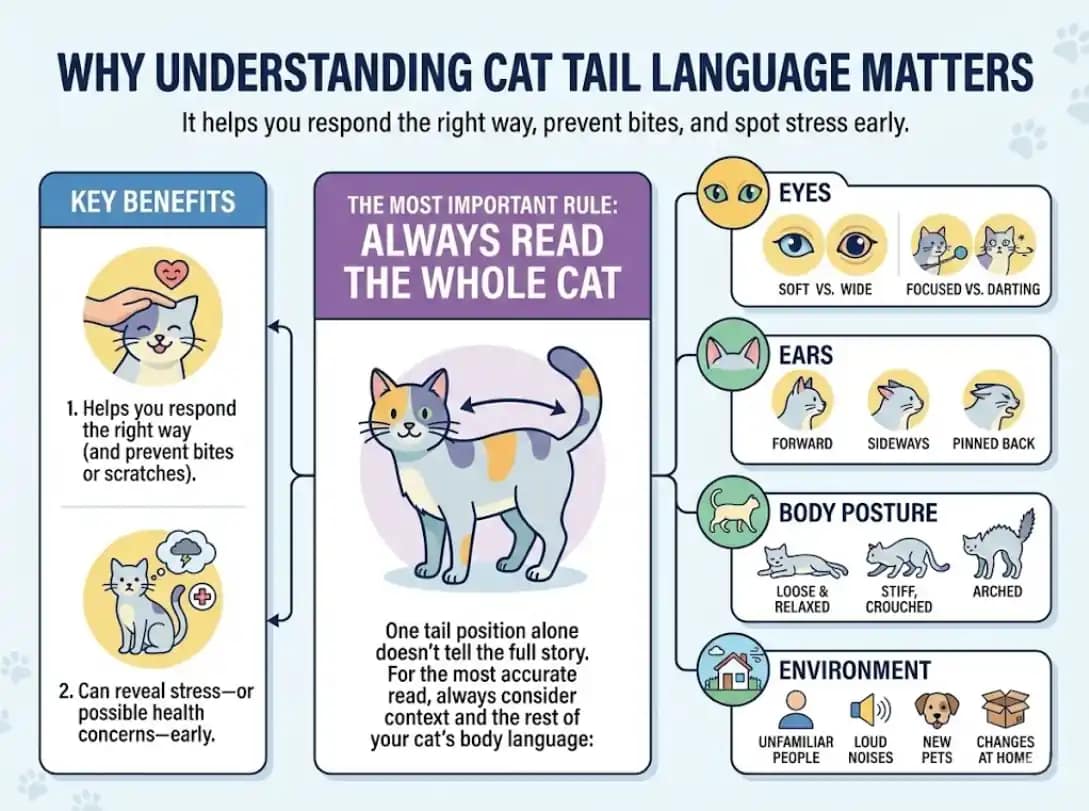
Why Understanding Cat Tail Language Matters
I still remember the first time I realized my cat was “talking” with her tail. She walked up with her tail held straight up, and I later learned that’s basically a feline Hallo—a sign of confidence, comfort, and friendliness.
A cat’s tail is one of the clearest parts of cat body language. Just like our facial expressions or tone of voice, tail positions and movements can signal happiness, curiosity, fear, irritation, stress, or even pain. When you learn how to read cat tail language, you’re not just decoding cute behavior—you’re understanding your cat’s emotional state in real time.
It helps you respond the right way (and prevent bites or scratches)
Knowing what your cat’s tail is saying can make everyday interactions smoother and safer. For example, if your cat’s tail starts thumping or lashing, that’s often a sign of overstimulation or annoyance. Pausing petting and giving space at that moment can prevent the situation from escalating into a swat or bite.
On the other hand, when your cat approaches with a “question mark” tail (upright with a curved tip), that’s commonly a friendly, playful invitation—your cat may be open to gentle interaction or a quick play session.
It can reveal stress—or possible health concerns—early
Tail language can also help you catch early warning signs. If a cat suddenly keeps the tail tucked, holds it unusually low, oder stops moving it, that can be a clue they’re feeling fear, stress, discomfort, or pain. While tail signals aren’t a diagnosis, noticing a “new normal” in tail behavior can prompt you to look closer and, when needed, talk to a veterinarian.
The most important rule: always read the whole cat
One tail position alone doesn’t tell the full story. For the most accurate read, always consider context and the rest of your cat’s body language:
Eyes: soft vs. wide, focused vs. darting
Ears: forward vs. sideways vs. pinned back
Body posture: loose and relaxed vs. stiff, crouched, or arched
Environment: unfamiliar people, loud noises, new pets, changes at home
When you “listen” to tail talk in context, you become a more attentive and compassionate cat parent—and your cat feels safer, understood, and more likely to trust you.
Now, let’s break down the most common cat tail positions and meanings—and what to do when you see each one.
Decoding Common Cat Tail Positions and What They Mean (With Quick Responses)
A cat’s tail is one of the clearest clues to their mood. In general, tail up = friendly/confident, tail puffed = scared/defensive, tail thrashing = irritated/overstimulatedund tail tucked = fearful or possibly in pain. The key is to read the tail together with ears, eyes, body posture, and the situation.
Quick Chart: Cat Tail Language at a Glance
Cat tail position / movement | What it usually means | What you should do |
|---|---|---|
Tail straight up | Friendly, confident greeting | Greet calmly; offer gentle pet/play |
Question-mark tail (curved tip) | Playful, curious, inviting | Initiate play; let them approach |
Relaxed tail held level/horizontal | Calm, comfortable | Continue normally; soft interaction OK |
Tail low or slinking | Uncertain, cautious | Give space; reduce stressors |
Tail tucked/clamped | Fear, distress (sometimes pain) | Stop interaction; create safety; consider vet if persistent |
Puffed “bottle brush” tail | Fear/defensive arousal | Back off; remove triggers; let them calm down |
Slow swish | Focused (hunting/curious) or mild uncertainty | Observe context; redirect into play if appropriate |
Fast thrash/thump | Annoyed/overstimulated; warning | Stop what you’re doing; give space |
Tip twitch/flick | Mild stimulation: focused oder slightly annoyed | Check ears/eyes; adjust interaction |
Tail wrap around you/another cat | Affection, bonding | Enjoy it; respond gently |
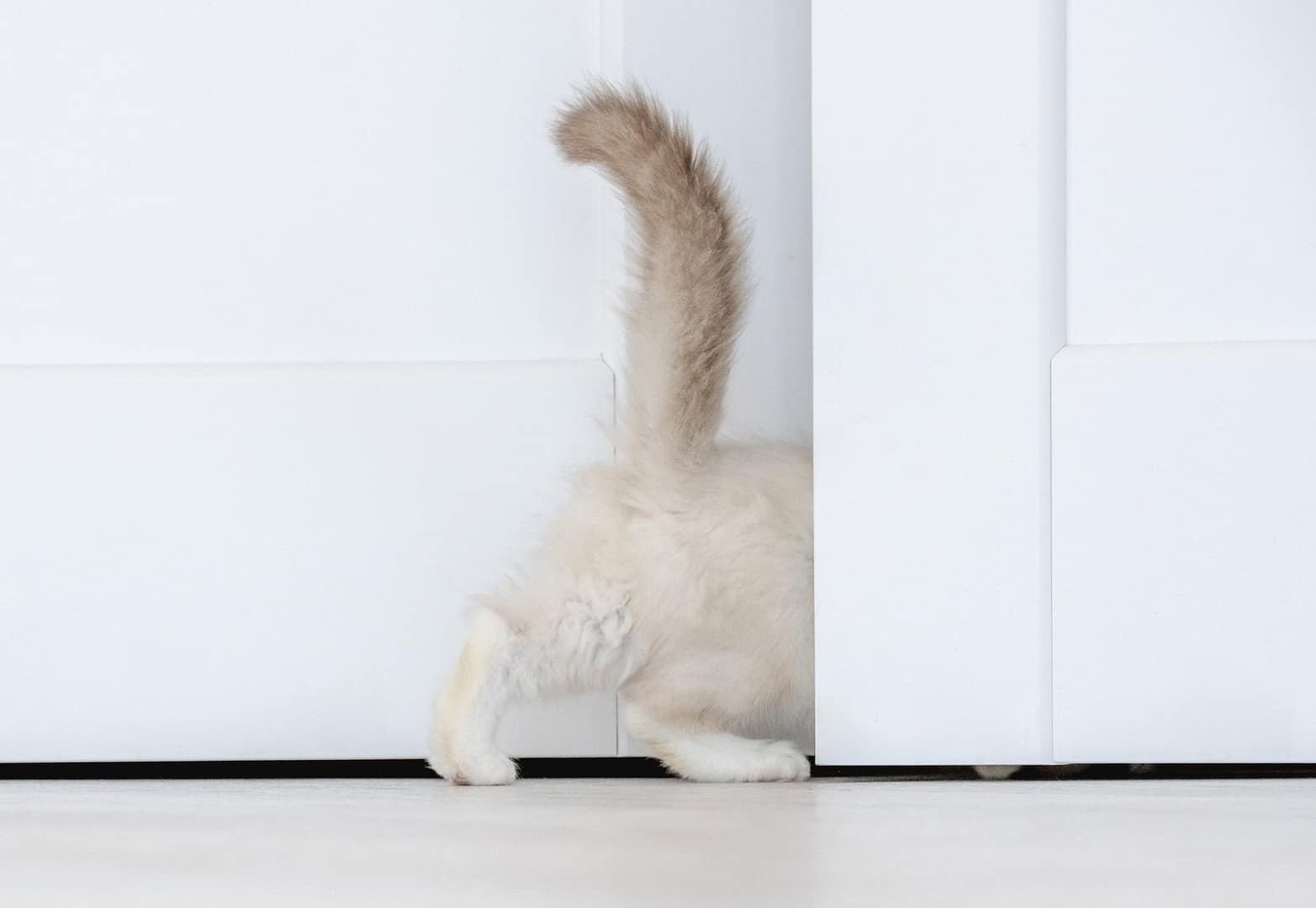
Tail Held High (Straight Up): Friendly Greeting + Confidence
Meaning: When your cat walks in with a tail held straight up, they’re usually feeling safe, confident, and social—it’s one of the most common “hello!” signals in cat body language.
What you’ll often see with it:
Relaxed body, ears forward
Soft eyes or slow blinking
A gentle rub against your legs
How to respond:
Use a calm voice
Offer cheek/chin scritches (many cats prefer this over tail touching)
If your cat seems energized, initiate a short play session
Question-Mark Tail (Curved Tip): Playful, Curious, “Let’s Interact”
Meaning: A tail that’s upright with a curved hook at the tip often signals friendly curiosity—your cat may be inviting attention or play.
Best response:
Let them approach and sniff your hand
Offer an interactive toy (wand toy, feather teaser, or a quick chase game)
Avoid: grabbing/booping the tail. Many cats don’t like tail handling—even when they’re happy.
Relaxed Horizontal Tail: “I’m Comfortable”
Meaning: A tail held level/horizontal (or gently lowered) with a loose body often means your cat is at ease.
Look for:
Loose posture, normal walking pace
Calm face, neutral ears
How to respond:
Gentle interaction is usually welcome
Keep your environment predictable and calm (especially in new spaces)
If the tail is horizontal but low: your cat may be unsure—see the next section.
Tucked Tail (Clamped or Wrapped): Fear, Distress (Sometimes Pain)
Meaning: A tail tucked tightly against the body is a strong signal: “I’m scared” oder “I’m uncomfortable.”
You may see this at:
Vet trips
Sudden scares (dogs, loud bangs, unknown people)
What to do immediately:
Stop interaction and give distance
Reduce noise, remove the trigger if possible
Speak softly; let them choose when to approach again
When to consider a vet visit: if tail tucking is persistent and paired with changes like hiding, reduced appetite, limping, or unusual aggression.
Puffed “Bottle Brush” Tail: Fear/Defensive Mode — Back Off
Meaning: A tail puffed up like a bottle brush (often with an arched back) signals intense fear or defensive arousal. Your cat is trying to look bigger to avoid danger.
How to respond safely:
Don’t approach, pet, or corner them
Separate them from other pets if needed
Let them retreat and calm down on their own timeline
Slow Swishing Tail: Focused Attention (Sometimes Mild Uncertainty)
Meaning: A slow side-to-side swish is commonly seen when a cat is focused—watching a bird, stalking a toy, or thinking.
How to interpret it:
If ears forward + eyes locked = hunting/playing focus (positive)
If ears rotating/back + tense body = mild annoyance or uncertainty
Was ist zu tun?
If it’s playful focus: redirect into play
If it’s uncertainty: reduce stimulation; give space
Fast Thrashing / Thumping Tail: Overstimulated, Annoyed, Warning Signal
Meaning: A fast, forceful tail lash or thump is one of the clearest “stop” signals in cat tail language.
Common scenario: petting too long → tail starts whipping → swat/bite risk increases.
Was ist zu tun?
Pause immediately
Give space
If needed, end the interaction calmly (no scolding)
Tail Tip Twitching / Quick Flicks: Mild Stimulation (Focus oder Irritation)
Meaning: A twitching tail tip often means your cat is mentally “on”—either focused on something, or mildly annoyed.
How to tell which:
Focus/excitement: eyes fixed, ears forward, body ready to pounce
Irritation: side-eye, ears slightly back, body stiffening
Best response:
If focus: channel it into play
If irritation: stop touching and let them reset
Tail Wrapped Around You (or Another Cat): Affection + Bonding
Meaning: A tail wrapped around your leg is basically a cat hug—a friendly, affiliative gesture.
Was ist zu tun?
Enjoy it Respond with calm affection
If it happens between cats, it’s usually a good sign of social bonding (especially during introductions)
Anmerkung: If tail wrapping comes with intense rubbing/spraying, it may be scent-marking—use context.
When Cat Tail Talk Signals Trouble: Red Flags to Watch For
Meistens, Katzen-Schwanz-Sprache reflects mood—curiosity, playfulness, irritation, or fear. But sometimes changes in your cat’s tail behavior can be an early warning sign of pain, injury, stress, or a medical issue.
If you’re a cat parent wondering, “Is this normal or should I call the vet?”—these are the tail signals worth taking seriously.
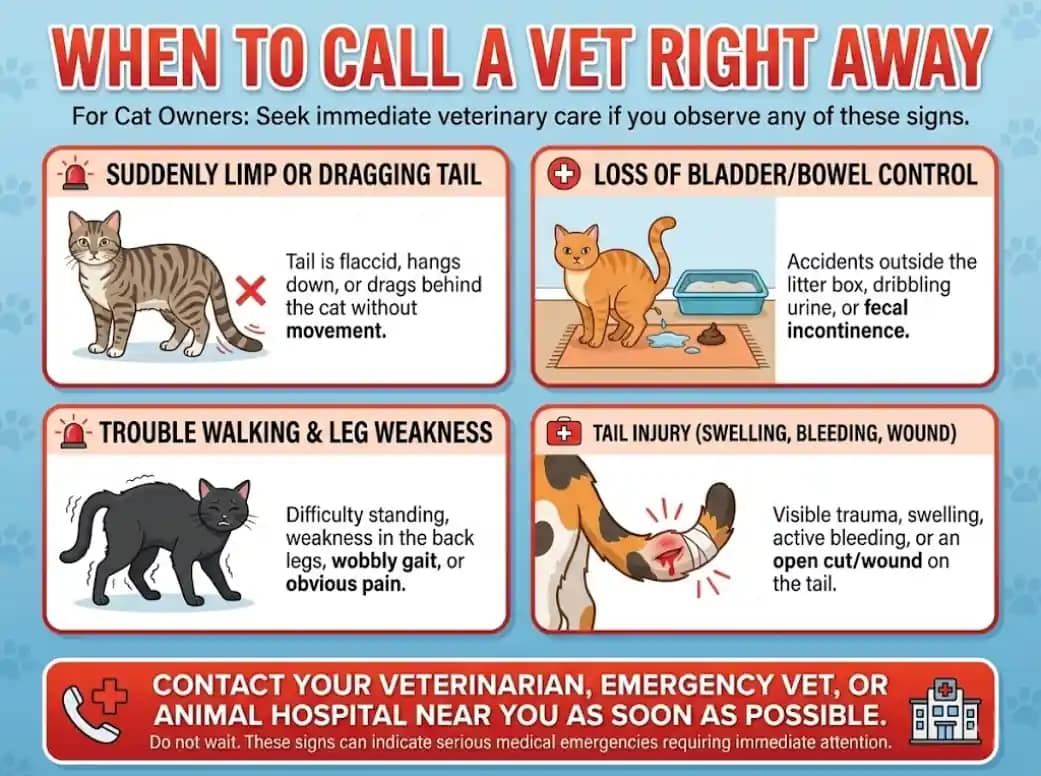
When to Call a Vet Right Away
Contact your veterinarian, emergency vet, or animal hospital near you as soon as possible if your cat has:
A suddenly limp or dragging tail
Loss of bladder/bowel control (accidents outside the litter box)
Trouble walking, weakness in the back legs, or obvious pain
A tail injury with swelling, bleeding, or an open wound
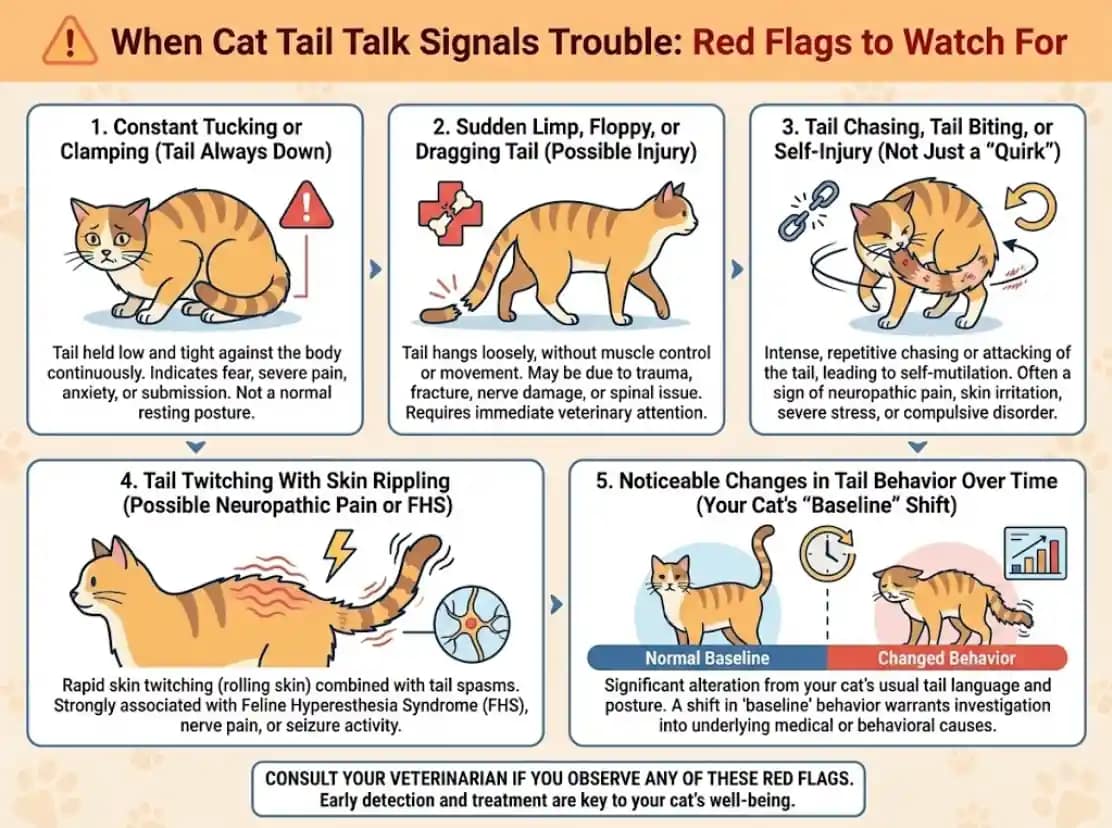
1. Constant Tucking or Clamping (Tail Always Down)
If your cat’s tail is persistently tucked under their body—even when nothing scary is happening—it can signal stress, fear, or discomfortund manchmal Schmerzen.
What it may mean
Joint pain (including Arthritis, especially in senior cats)
Abdominal discomfort
Ongoing stress or anxiety
What to watch for
Hiding more than usual, reluctance to jump, decreased play
Hunched posture, flattened ears, “tight” body language
Was ist zu tun?
Reduce stressors (noise, new pets, guest traffic) and give quiet hiding spots
If the tucked tail is frequent or paired with behavior changes, book a vet appointment to rule out pain-related causes
2. Sudden Limp, Floppy, or Dragging Tail (Possible Injury)
A tail that suddenly goes limp, droops, or drags is not typical. This can be a sign of tail trauma oder nerve damage, especially near the tail base.
Common causes
Tail caught in a door
A fall or rough handling (tail pulled)
Bite wounds or other injuries
Red flags that make this urgent
Difficulty walking or weak back legs
Pain when the tail base is touched
Litter box accidents or constipation
Was ist zu tun?
Avoid touching or “testing” the tail—your cat may be in pain
Keep them calm and confined
Seek veterinary care promptly, especially if mobility or bathroom habits change
3. Tail Chasing, Tail Biting, or Self-Injury (Not Just a “Quirk”)
Kittens may chase tails during play, but in adult cats, obsessive tail chasing oder biting the tail until it’s sore can point to an underlying issue.
Possible causes
Fleas, allergies, or skin irritation (itch-driven behavior)
Anxiety or compulsive behavior
Felines Hyperästhesie-Syndrom (FHS) (“twitchy cat syndrome”)
Cats with FHS may have sudden episodes of:
Skin twitching along the back
Tail whipping
Zooming, agitation, or sensitivity to touch near the spine
Was ist zu tun?
Check for fleas and skin irritation (and treat if needed)
If your cat repeatedly targets their tail or breaks skin, einen Tierarztbesuch vereinbaren—don’t wait for it to “pass”
4. Tail Twitching With Skin Rippling (Possible Neuropathic Pain or FHS)
If your cat’s lower back skin ripples and the tail flicks rapidly—especially with no obvious trigger—this may be more than normal stimulation.
Wie es aussehen kann
Sudden rippling along the spine
Tail flicking that seems “out of control”
Vocalizing, dashing, or reacting sharply if touched
Helpful tip for diagnosis
Record a short video of the episode to show your veterinarian—this can help rule out skin issues, pain, or neurological causes
Was ist zu tun?
Avoid touching the sensitive area during an episode
Book a vet appointment if episodes repeat or escalate
5. Noticeable Changes in Tail Behavior Over Time (Your Cat’s “Baseline” Shift)
Every cat has a normal “tail baseline.” Maybe yours greets you with a tail held high, or lazily swishes when relaxed. When that baseline suddenly changes, it can signal stress, chronic pain, or illness.
Common triggers
Moving, new pets, new scents, schedule changes, construction noise
Aging (reduced tail motion may occur with Arthritis)
What to watch for
Tail held low more often than usual
Less social behavior, reduced activity, irritability
New sensitivity when touched
Was ist zu tun?
Note when the change started and what else changed in the home
If the shift lasts more than a few days or comes with other symptoms, check in with your vet
Vertraue deinem Bauchgefühl, vertraue ihrem Schwanz
If your cat’s tail behavior feels “off,” it’s worth paying attention. A limp tail, a chronically tucked tail, intense tail twitching, oder self-injury can be your cat’s way of signaling discomfort, distress, or a medical problem.
Cats are subtle—but they’re always communicating. Learning these cat tail warning signs helps you respond early, protect your cat’s health, and keep them feeling safe.
Conclusion: Listening to What Your Cat’s Tail Is Telling You
By now, you’ve explored the most common cat tail positions and meanings—from a tail held high in a confident greeting to a fast lash that signals “I’ve had enough,” from affectionate tail wraps to the dramatic bottle-brush tail that shows fear or high alert.
The real goal isn’t to memorize every movement like a test. It’s to get better at reading cat tail language in context—along with your cat’s ears, eyes, body posture, and environment—so you can respond in a way that helps your cat feel safe, understood, and respected.
When you notice your cat’s tail starting to flick and you pause petting, you’re not just avoiding a scratch—you’re building trust. When you recognize a playful, upright tail and offer a short play session, you reinforce positive feelings and strengthen your bond. Over time, your cat learns that you “get it,” and many cats become even more expressive once they feel listened to.
Most importantly, tail signals can also help you spot trouble early. If your cat’s tail behavior changes suddenly—stays tucked, goes limp, or becomes unusually twitchy—treat it as a clue to check for stress, pain, or an underlying health issue.
Your cat may not speak human language, but they’re always communicating. And once you understand what different cat tail movements mean, you’ve added one of the most practical tools in your everyday cat-care toolkit.
FAQs: Understanding Cat Tail Language
Was bedeutet es, wenn eine Katze ihren Schwanz gerade nach oben streckt?
Ein gerade nach oben gehaltener Schwanz deutet in der Regel auf Freundlichkeit, Selbstvertrauen und Interaktionsbereitschaft hin. Es handelt sich um eine übliche Begrüßungshaltung, die oft zu beobachten ist, wenn Ihre Katze sich freut, Sie zu sehen.
Warum wedelt oder schlägt meine Katze plötzlich mit dem Schwanz?
Schnelle Schwanzbewegungen sind in der Regel ein Zeichen für Gereiztheit oder Überreiztheit. Wenn Ihre Katze mit dem Schwanz schlägt, während Sie sie streicheln, sollten Sie am besten aufhören und ihr Freiraum lassen.
Sollte ich mir Sorgen machen, wenn die Schwanzhaltung meiner Katze immer niedrig oder eingezogen ist?
Ja, ein chronisch gesenkter oder eingezogener Schwanz kann auf Angst, Stress oder sogar Schmerzen hindeuten. Wenn Ihre Katze diese Haltung häufig einnimmt und Aktivitäten oder soziale Interaktionen meidet, konsultieren Sie einen Tierarzt.
Kann das Schwanzverhalten auf medizinische Probleme bei Katzen hinweisen?
Auf jeden Fall. Eine schlaffe Schwanzhaltung, übermäßiges Jagen oder Zuckungen, begleitet von Hautwellen, können auf Nervenschäden, Hyperästhesie-Syndrom oder Verhaltensstörungen hinweisen und sollten von einem Tierarzt untersucht werden.
Ist die Schwanzsprache bei allen Katzenrassen gleich?
Obwohl die Kernmerkmale ähnlich sind, können rassespezifische Merkmale (wie die Schwanzlosigkeit der Manx-Katze oder die gekräuselten Schwänze der amerikanischen Ringtail-Katze) die Ausprägung beeinflussen. Beobachten Sie immer die Muster Ihrer individuellen Katze, um ein bestmögliches Verständnis zu erlangen.
Referenzen
Brincat, C. (7. Dezember 2024). Kommunizieren Katzen mit ihren Schwänzen? Live-Wissenschaft. https://www.livescience.com/animals/domestic-cats/do-cats-communicate-with-their-tails
Gerken, A. (26. November 2023). Wie Sie die Schwanzsprache Ihrer Katze lesen können. PetMD. https://www.petmd.com/cat/behavior/cat-tail-language
Lesté-Lasserre, C. (15. November 2024). Miau! Gewellte Schwänze verleihen Katzen einen “Akzent”.”. Wissenschaftliche Amerikanerin. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/curly-tailed-cats-communicate-with-an-accent/
Marek, R. (o. J.). Geschichten über die Gefühle von Katzen erzählen. Angstfreie, glückliche Zuhause. https://www.fearfreehappyhomes.com/telling-tails-about-cat-emotions/
PetMD-Redaktion. (10. August 2017). 7 häufige Verletzungen am Schwanz von Katzen. PetMD. https://www.petmd.com/cat/emergency/accidents-injuries/7-common-cat-tail-injuries